What is Micromeritics?
The Science and Technology of
small particles is known as Micromeritics.
Micromeritics deals with-
• Particle
size and Size Distribution
• Methods of Determining particles size
• Particle shape and surface area
• Pore size
Importance of Study of Micromeritics
Knowledge and control of the
size and the size range of particle is of profound importance in pharmacy.
Size and surface area can be
related to the physical, chemical and pharmacological properties of a drug.
1.Particle size affect its
release from dosage forms that are administered orally, parenterally, rectally and topically
2. Physical stability and
pharmacologic response of suspensions, emulsion and tablets depends on particle
size.
3. It is also important in flow
properties and proper mixing of granules and. powders in tableting.
4. Both Tablets and capsules are
produced using equipment which controls the mass of drug and other particles by
volumetric filling. Therefore any interference with the uniformity of fill
volumes may alter the mass of drug incorporated into the tablet or capsules.
Thus reduce the uniformity of the medicine.
5. Powders with different
particle sizes have different flow and packing properties which alter the
volumes of powder during each encapsulation or tablet compression.
6.The
rate of solution depends on the several factors. One factor is the particle
size. Thus particles having small dimensions will tend to increase the rate of
solution.
For
example:
a). Griseofulvin has a low solubility by oral
administration but is rapidly distributed following absorption. The solubility
of Griseofulvin can be greatly increased by
particle size reduction.
b).
Reduction of particles size also increase the rate of absorption of
tetracycline, Aspirin and Sulphonamides.
c).
Reduction of particle size of nitrofurantoin increased the rate of
absorption. Therefore the toxic effect due to rapid absorption.
Different means of
expressing particle size.
There are
different means of expressing particle size:
Millimeter (mm)……. 10-3 meter
Micro
meter (µ m) ……. 10-6 meter
nano meter (nm)…….. 10-9 meter
pico meter ……………10-12 meter
fanto
meter………………... 10-15 meter
Particle
Dimension in Pharmaceutical Disperse system
Particle
size
Micrometer (µ m) Millimeter (mm) Disperse systems
0.5-10 0.0005 - 0.010 Suspension,
fine emulsion
10-50 0.010- 0.050 Coarse
emulsion, flocculated suspension
50- 100 0.50- 0.100 Lower
range of sieve range, fine powder range
150-1000 0.150-1.000 Coarse
powder range
1000- 3360 1.000- 3.360 Average
granule size
Methods of determining
particle size
- Optical
Microscopy
- Sieving
Methods
- Sedimentation
Methods
Particle
volume measurement:
- Coulter Counter
Method (Electrical stream sensing method)
- Laser light
scattering methods.
Methods of determining surface
area:
- Adsorption method
- Air permeability method
Sieving Method
Sieving method
is an ordinary and simple method. It is widely used as a method for the
particle size analysis.
Range of analysis:
The
International Standards organization (ISO) sets a lowest sieve diameter of 45 µm and sincepowders are usually defined as having a maximum diameter of 1000 µm, this could
be considered to be the upper limit.
In practice
sieves can be obtained for size analysis over a range from 5 to 125 000 µm.
 |
| Particle diameter
Sample
preparation and analysis condition
|
1. Sieve analysis is usually
carried out using dry powders.
2. Although, for powders in
liquid suspension or which agglomerate during dry sieving, a process of wet
sieving can be used.
Principle of Measurement:
Sieve analysis utilizes a woven, punched or electroformed mesh often in
brass, bronze or stainless steel with known aperture (hole) diameters which
form a physical barrier to particles.
Most sieve analyses utilize a series, stack (
Load /Mountain or nest (layer) of sieves which have the smallest mesh above a
collector tray followed by meshes which get progressively coarser towards the
top of the series.
A sieve stack usually comprises 6-8 sieves with a
progression based on a √2 or 2√2 change in diameter between adjacent aperture.
Powder
is loaded on to the coarsest sieve of the assembled stack and the nest is
subjected to mechanical vibration for, say 20 minutes
After
this time , the particles are considered to be retained
on the
sieve mesh with an aperture corresponding to the minimum or sieve diameter.
A
sieving time of 20 minutes is arbitrary and BS 1796 recommends sieving to be
continued until less than 0.2% material passes a given sieve aperture in any 5
minutes interval
Advantages : 1. This method is very simple.
2. Not expensive
3. Easy to operate
Disadvantages: 1. Not
too much precise method.
2. Not
applicable for all disperse systems.
Sedimentation Methods
Sedimentation Method is also an ordinary and
simple method.
It is widely
used as a method for the particle size analysis.
Range of analysis:
Sample preparation and analysis conditions
In this method particle size can be
determined by examining the powder as it sediments out.
(a). In cases where the powder
is not uniformly dispersed in a fluid it can be introduced as a thin layer on
the surface of the liquid.
(b). If the powder is lyophobic, e.g. hydrophobic in water ,
it may be necessary to add dispersing
agent to aid wetting of the powder.
(c). In case where the powder
is soluble in water it will be necessary
to use non- aqueous liquids or carry out the analysis in a gas.
Principle of Measurement
Particle
size analysis by sedimentation method can be divided into two main categories according to the method
of measurement used.
1. One of the type is based on
measurement of particle in a retention zone.
2. Another type uses a
non-retention measurement zone.
An example of a non-retention zone
measurement is known as the pipette method.
In this method , known
volumes of suspension are drawn off and the
concentration differences are measured with respect to time.
One of the most popular of the pipette methods
was that developed by Andreasen and Lundberg and commonly called the Andreasen pipette.
The Andreasen fixed-position pipette consists of a 200 mm
graduate cylinder which can hold about 500 ml of suspension fluid.
A pipette is located centrally
in the cylinder and is held in position by a ground glass stopper so that its tip coincides with
the zero level.
A three way tap allows fluid
to be drawn into a 10 ml reservoir which can then be emptied into a beaker or
centrifuge tube.
The amount of powder can be
determined by weight following drying or centrifuging.
The
weight of each sample residue is
therefore called the weight of undersize and the sum
of the successive weight is known as the
cumulative weight of
undersize. It can be
expressed directly in weight units or percent of the total weight of the final
sediment..
The data of cumulative weight of undersize
is used for the determination of particle weight distribution, number
distribution,
The largest particle diameter in each sample is then
calculated from Strokes’
Law.
The
particle size may be obtained by gravity sedimentation as expressed in Strokes’
law.
Where ,
v = rate of settling
h = Distance of the fall in time , t
dst = the mean diameter of the particles
based on the velocity of sedimentation
ρs= density of
the particles
ρo = density of
the dispersion medium
g
= Acceleration due to gravity
ηo = Viscosity of the medium
Note: The
question holds spheres falling freely without hindrance and at a constant rate.
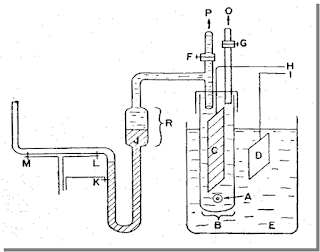
Coulter Counter Method (Electrical
stream sensing zone method)
Coulter
Counter Method (Electrical stream sensing zone method) is a
sophisticated method. It is a precise
and accurate method.
Range of analysis:
Sample preparation and
analysis
conditions
1. Powder samples are dispersed in an
electrolyte to form a very dilute suspension
2. The suspension is usually subjected to ultrasoni agitation for a period to break up any particle agglomerates.
3. A dispersant may also be added to aid particl deagglomeration.
2. The suspension is usually subjected to ultrasoni agitation for a period to break up any particle agglomerates.
3. A dispersant may also be added to aid particl deagglomeration.
Principle
of Measurement
1.The particle suspension is drawn through an aperture
accurately drilled through a sapphire crystal set into the wall of a hollow
glass tube.
2. Electrodes, situated on either side of the aperture and
surrounded by an electrolyte solution.
3. Monitor the change in electrical signal which occurs
when a particle momentarily occupies the orifice and displaces its own volume
of electrolyte..
4. The volume of suspension drawn through the orifice is
determined by the suction potential created by a mercury thread rebalancing in
a convoluted U tube.
5.The volume of electrolyte fluid which is displaced in the
orifice by the presence of a particle causes a change in electrical resistance
between the electrodes which is proportional to the volume of the
particle.
6.The
change in resistance is converted between into a voltage pulse which is
amplified and processed electronically .
7.
Pulses falling within pre-calibrated limits or thresholds are used to split the particle size distribution
into many different size ranges.
In
order to carry out size analysis over a wide diameter range it will
be necessary to change orifice diameter
used, to prevent
Coarse
particles blocking a small diameter orifice . Conversely, finer particles in a
large diameter orifice will cause too small a relative in volume to be accurately
quantified.
Advantages : 1. It is one of the
precise and accurate method.
2. Analysis range is wide.
Disadvantages: 1. It is a sophisticated
method.
2. It is a expensive
method.





EmoticonEmoticon